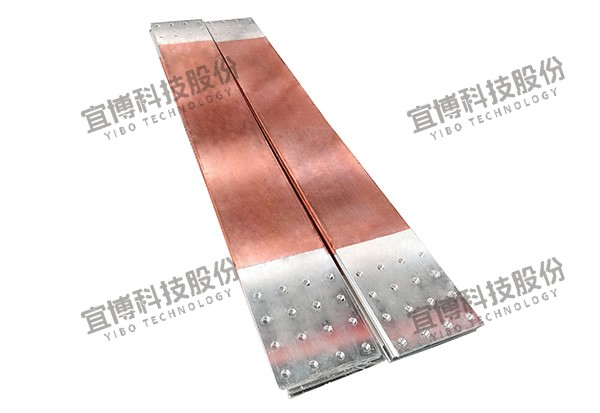
Copper-Aluminum Transition: Innovating Materials for Efficient Power Transmission
Copper-to-Aluminum Transition: Innovating Materials for Efficient Power Transmission
The ongoing evolution of power transmission systems is driving significant advancements in materials science. Among these, the copper-to-aluminum transition (Cu-to-Al transition) stands out as a key innovation, offering a blend of performance, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. This article explores the significance of Cu-to-Al transitions, their applications, and the challenges and opportunities they present in the power industry.
The need for efficient and cost-effective power transmission has never been greater. Traditional copper conductors, while highly conductive, are expensive and heavy. Aluminum, on the other hand, offers similar electrical conductivity at a lower cost and weight. However, the direct use of aluminum in high-current applications can lead to galvanic corrosion and other issues when in contact with copper. This has led to the development of Cu-to-Al transition technologies, which allow for the seamless integration of aluminum and copper in power transmission systems.
Technical Aspects and Applications:
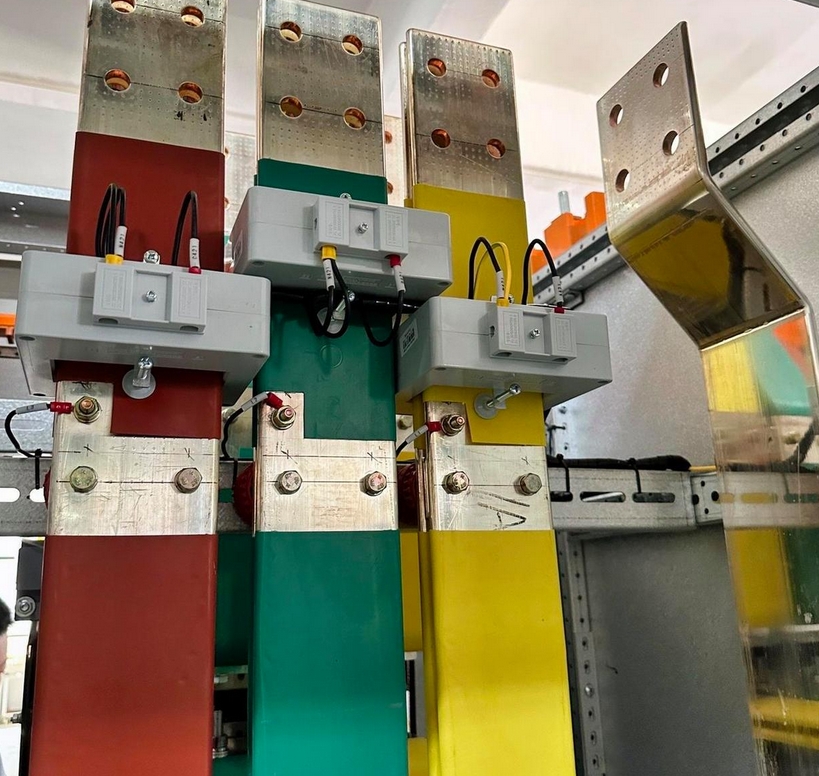
Cu-to-Al transitions are achieved through specialized connectors, terminals, and splices designed to bridge the gap between copper and aluminum conductors. These transitions are critical in ensuring that the two metals do not corrode or degrade when joined, maintaining the integrity and efficiency of the power transmission system.
In overhead power lines, Cu-to-Al transitions are used to connect aluminum conductors with copper-based equipment, such as transformers and distribution cables. This reduces the overall weight of the line and lowers installation and maintenance costs. Similarly, in underground power cables, Cu-to-Al transitions enable the use of aluminum conductors in sections where weight and cost are critical factors.
Challenges and Solutions:
Despite their benefits, Cu-to-Al transitions face challenges related to galvanic corrosion and material compatibility. Galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals are connected in an electrolytic environment, leading to the accelerated deterioration of one or both metals. To mitigate this, manufacturers have developed specialized coatings and treatments that isolate the metals and prevent corrosion.
Advancements in material science are also addressing compatibility issues. New alloy compositions and surface treatments are being developed to enhance the adhesion and corrosion resistance of Cu-to-Al transitions. These innovations are crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of power transmission systems.
Market Trends and Future Prospects:
The growing demand for sustainable and cost-effective power transmission solutions is driving the market for Cu-to-Al transitions. As utilities and energy companies seek to reduce their carbon footprints and operational costs, the adoption of aluminum conductors and Cu-to-Al transitions is accelerating.
Moreover, the increasing deployment of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, is creating new opportunities for Cu-to-Al transitions. These renewable energy systems often require longer transmission lines and more connections, making Cu-to-Al transitions an essential component for ensuring efficient and reliable power delivery.
The Cu-to-Al transition represents a significant innovation in power transmission systems, offering a practical solution to the challenges of cost, weight, and sustainability. By enabling the seamless integration of aluminum and copper conductors, Cu-to-Al transitions are enabling more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly power transmission. As technological advancements continue to address material compatibility and corrosion issues, the future of Cu-to-Al transitions in the power industry looks promising.